
Ejector TheoryĪnother important thing to check during ejector installation is external loads Piping load act on the ejectors.
#Ejector design calculation software manual
Hence it very important to provide a drain valve installed at low points can be either manual or automatic float operated valves. Since any condensed or solid particles may reduce throughput capacity of the ejectors.

However, it is very important to provide a provision to remove the condensate or solid particles from the entrained gases of the ejector. Ejectors may be installed at any orientation. By the required capacity is very high then two or three ejectors are working in parallel. The capacity of an ejector is determined by its dimensions. Normally the discharge pressure will be 10 to 15 times of the suction pressure. Thereby the mixture gained higher pressure send to the atmosphere or some closed system. The velocity of the fluid at the mixing chamber is approximately to metres per second. When the suction fluid starts mix with the motive fluid in the mixing chamber. The motive fluid will create a vacuum in the mixing chamber refer the pressure curve where the pressure is decreased and velocity is increased. The suction line of the ejector is connected to the vessel which is to the kept under low pressure. In mixed fluid enter the diverging portion of the ejector where its velocity energy is converted into Pressure energy. Saggi e cappelliĭue to the low-pressure zone, the suction fluid will start to move to toward it and mix with motive fluid in the mixing chamber. Due to the pressure drop of the motive fluid, it will create a low-pressure zone before the mixing chamber.
#Ejector design calculation software free
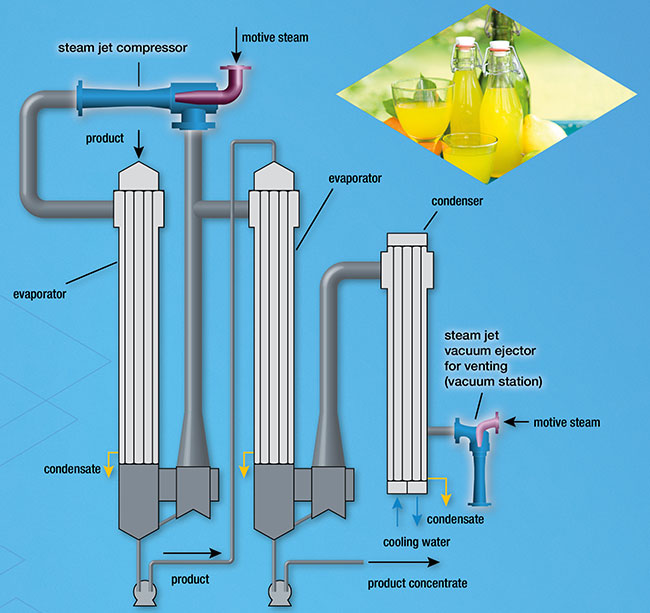
Hence it is relatively low-cost and easy to operate and maintenance free equipment. The major difference between the ejector and the vacuum pump or compressor is it had no moving parts. An ejector is similar to an of vacuum pump or compressor. Motive flow and suction flow are mixed at supersonic velocity and then decelerated to the sonic velocity upon reaching the diffuser throat.An ejector is a device used to suck the gas or vapour from the desired vessel or system. The steam velocity exceeds the sonic velocity accordingly. The diffuser converts the kinetic energy of the mixture consisting of motive flow and suction flow back into static pressure energy. This kinetic energy can be released to the suction flow by impulse transfer while both flows mingle. The increase from suction pressure ps to discharge pressure p d corresponds to the delivery head for the suction flow or to the pressure difference of the jet ejector. Motive flow and suction flow pass together - as a mixture - through the diffuser, loosing velocity and gaining pressure. Part of the kinetic energy is transferred to the suction flow. At this point the suction flow enters into the ejector head 3 through the suction connection B and is mixed with the motive fluid flowing with high velocity. The pressure in the motive nozzle 2 decreases and the velocity rises. The flow section will change along this path. The motive fluid passes successively through these two components. The application determines the design of the flow section.Ī steam jet ejector is illustrated below as example steam serves as motive fluid to create vacuum. This basic principle applies to every jet ejector in different models and ranges of application. A jet ejector requires no mechanical drive and has no moving parts. The term jet ejector describes a device in which a pumping effect is achieved using a motive fluid. The lower sectional model shows the internal construction of a jet pump which generates a vacuum on the suction side by means of steam as a motive medium. The application field determines the shape of the flow cross-section which is designed individually dependent on the motive medium. The pumping effect is generated by means of a liquid or gaseous motive medium acting as energy carrier. They are designed in a multitude of materials and optimised for their application purposes.

A jet pump works without a mechanical drive and therefore offers high reliability in continuous operation mode. Each ejector is individually designed for its application and optimally suited for the specific use.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
